Resources
Abstract
High-Dynamic-Range Wide-Color-Gamut (HDR-WCG) technology is becoming increasingly widespread, driving a growing need for converting Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) content to HDR. Existing methods primarily rely on fixed tone mapping operators, which struggle to handle the diverse appearances and degradations commonly present in real-world SDR content. To address this limitation, we propose a generalized SDR-to-HDR framework that enhances robustness by learning attribute-disentangled representations.
Central to our approach is RealRep, which explicitly disentangles luminance and chrominance components to capture intrinsic content variations across different SDR distributions. Furthermore, we design a Luma-/Chroma-aware negative exemplar generation strategy that constructs degradation-sensitive contrastive pairs, effectively modeling tone discrepancies across SDR styles. Building on these attribute-level priors, we introduce the Degradation-Domain Aware Controlled Mapping Network (DDACMNet), a lightweight, two-stage framework that performs adaptive hierarchical mapping guided by a control-aware normalization mechanism. DDACMNet dynamically modulates the mapping process via degradation-conditioned features, enabling robust adaptation across diverse degradation domains.
Methodology
01 Attribute Disentanglement & Negative Generation
SDR images exhibit distinct luminance and chrominance distributions under different degradations. Traditional methods often learn entangled features, leading to poor generalization.
As shown in Figure 1(a), RealRep introduces a contrastive multi-view encoder to explicitly separate luminance and chrominance. We utilize a novel Luma-/Chroma-aware negative exemplar generation strategy to construct degradation-sensitive contrastive pairs, forcing the model to learn style-invariant content representations and style-specific attribute representations.
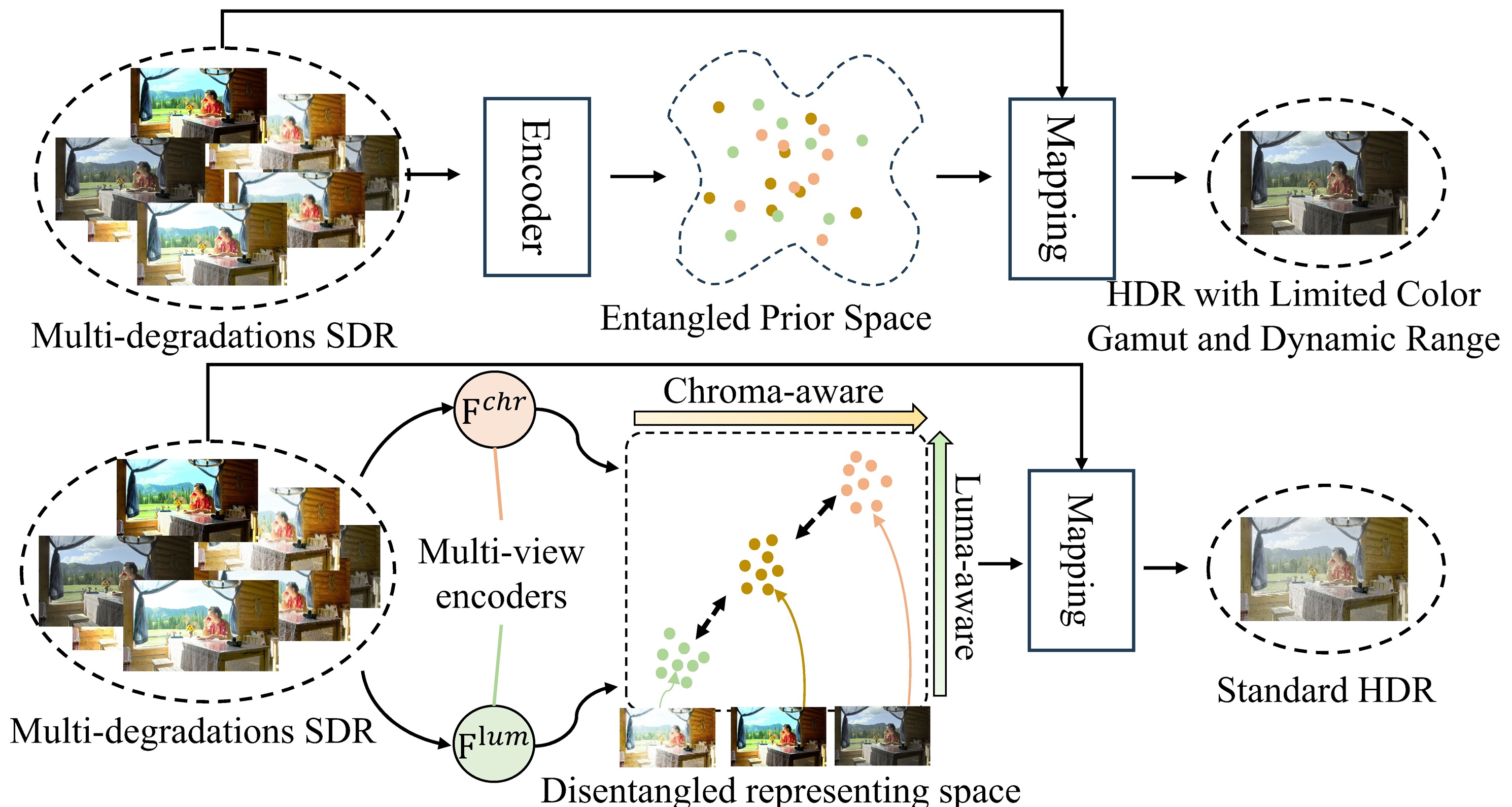
Figure 1(a): Comparison between previous entangled frameworks (top) and our attribute-disentangled method (bottom).
02 Degradation-Domain Aware Controlled Mapping (DDACMNet)
To fully leverage the disentangled priors, we design DDACMNet. It consists of two key stages:
- Dense Controlled Mapping (DCM): Handles global tone mapping by utilizing global degradation priors for affine transformations.
- Sparse Controlled Mapping (SCM): Handles local detail enhancement, utilizing spatially varying local features for fine-grained adjustment.
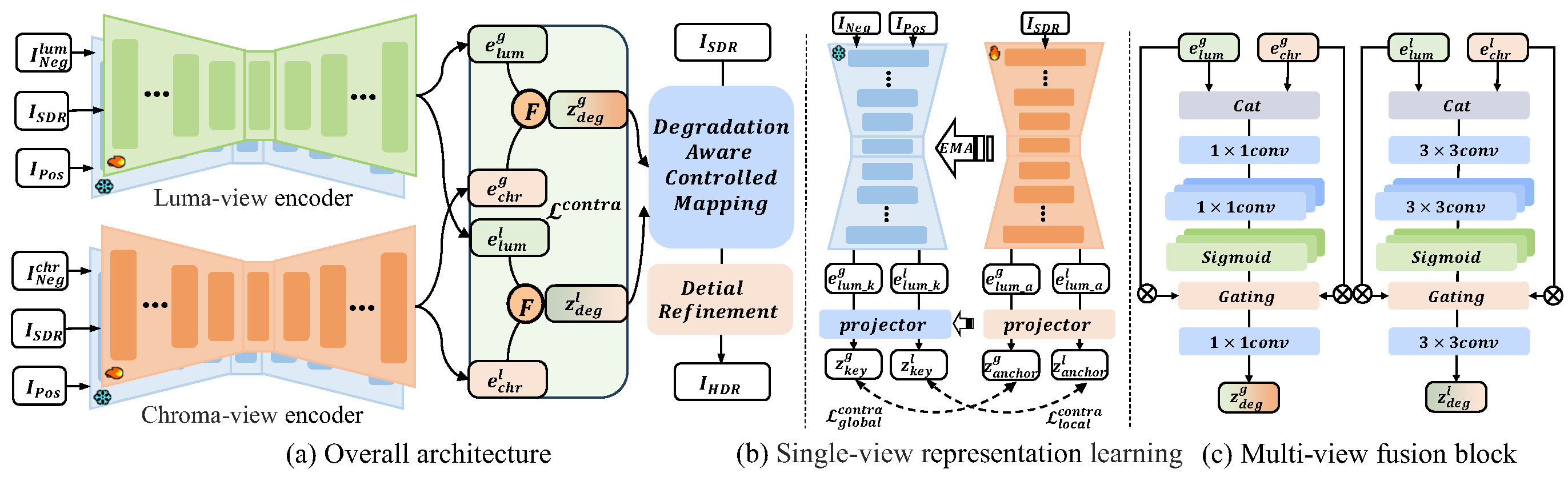
Figure 2: Overview of the DDACMNet architecture. It consists of multi-view encoders, a fusion module, and a controlled mapping network.
Feature Space Analysis
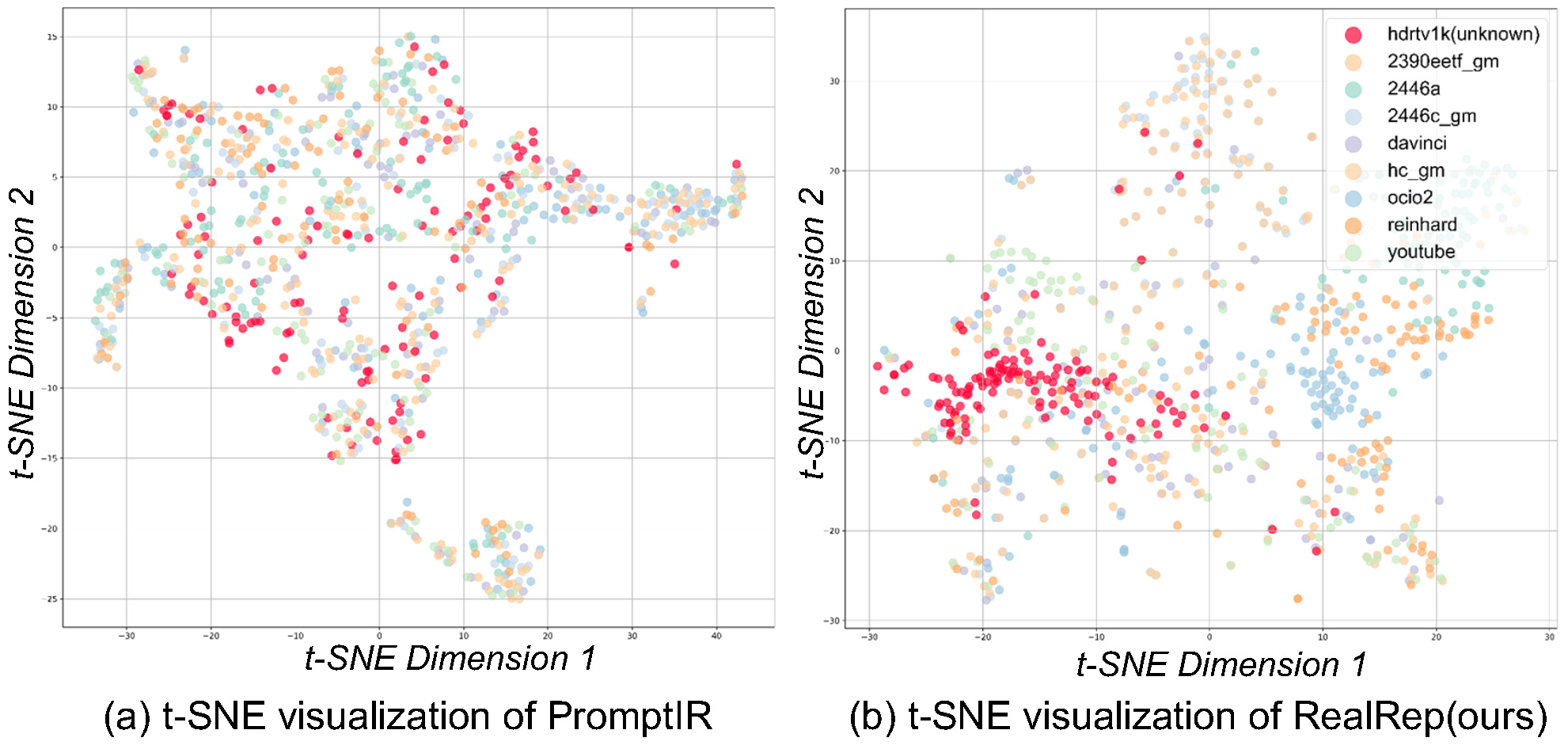
Why is RealRep More Robust?
Through t-SNE visualization (Figure 6 in the paper), we can clearly see the advantages of RealRep in constructing the feature space.
Compared to other methods (e.g., PromptIR) which show chaotic and overlapping feature distributions under unknown degradations, RealRep generates compact and well-separated feature clusters. This demonstrates that our disentangled learning strategy successfully separates features of different degradation types, enabling the model to accurately match the closest degradation prior when facing unseen real-world SDR styles, thereby achieving robust conversion.
Experiments
Quantitative Comparison
| Methods | 2390eetf.gm | 2446a | 2446c.gm | davinci | hc_gm | ocio2 | reinhard | youtube | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDRTVNet | 28.97 / 0.90 | 23.73 / 0.85 | 26.05 / 0.86 | 25.50 / 0.88 | 26.91 / 0.86 | 26.46 / 0.87 | 23.23 / 0.87 | 25.31 / 0.87 | 25.77 / 0.8716 |
| LSNet | 33.23 / 0.94 | 31.18 / 0.91 | 28.05 / 0.87 | 25.63 / 0.90 | 27.34 / 0.87 | 29.56 / 0.89 | 25.67 / 0.90 | 27.01 / 0.90 | 28.46 / 0.8979 |
| RealRep (Ours) | 34.13 / 0.95 | 34.41 / 0.93 | 30.38 / 0.89 | 30.05 / 0.93 | 30.47 / 0.90 | 31.36 / 0.91 | 27.59 / 0.93 | 30.03 / 0.94 | 31.05 / 0.9219 |
Note: The table shows PSNR / SSIM results on the HDRTV4K dataset. Our method achieves the best performance across all subsets.
Qualitative Results
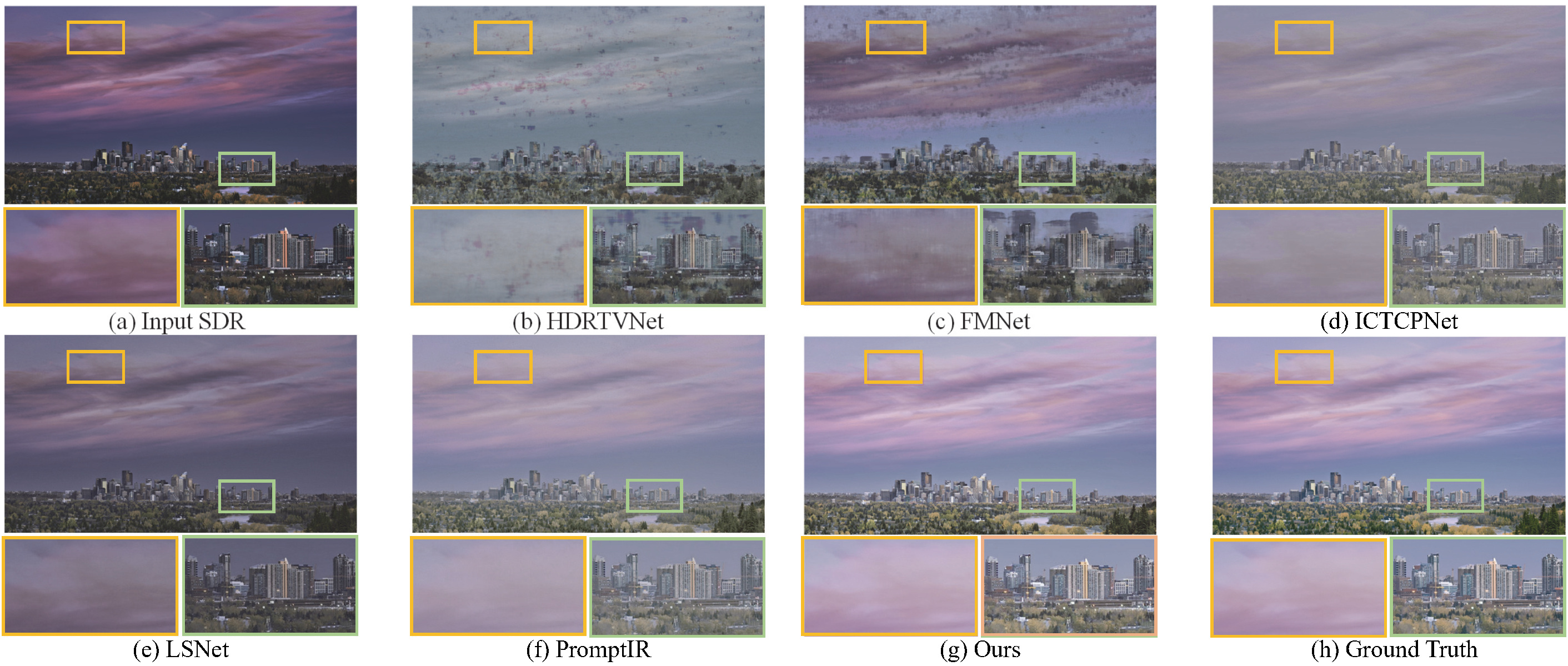

When facing unknown degradations (e.g., complex real-world lighting and tone mapping), RealRep demonstrates superior stability. Compared to methods like LSNet and ICTCPNet, our model not only eliminates artifacts but also accurately recovers highlight details and color saturation, generating visually more natural and vivid HDR images.